Invasive alien species (IAS) threaten livelihoods and biodiversity globally
Invasions from non-native plants, animals and pathogens threaten the economies of the world’s poorest nations, according to a new study. The study, published in Nature Communications (‘Global threats from invasive alien species in the twenty-first century and national response capacities’) found that one-sixth of the world’s land is highly vulnerable to invasion, including substantial areas…
CABI at EcoSummit 2016
CABI promoted its new invasive species initiative at this year’s EcoSummit event which took place in Montpellier, France, from 29 August – 1 September. CABI’s latest initiative aims to tackle the issue of invasive species to improve the lives of 50 million farmers in Africa and Asia. Launched in Copenhagen in 1996, the event provides…
New European Union IAS Regulation
Invasive alien species are a major threat worldwide, impacting upon millions of livelihoods and threatening biodiversity. The situation is worsening, due in no small part to increased global trade and transport. The economic costs of IAS can be vast: worldwide, invasive species are estimated to cost US$1.4 trillion per year – close to 5% of global…
The three Cs of the Invasives’ programme development: concepts, compromise and coffee
Since March 2016, I have been working as the programme support manager for the multi-sectorial development initiative called the Invasives programme. Our new Invasives initiative will be undertaking regional, national and local technical and partnership activities to deal with some of the worst biological invasions that are threatening livelihoods in poor rural areas. As we…
A fifth of the world’s plants under threat, as report says 391,000 species now known to science
Dave Simpson – 11 May 2016 A ground-breaking report from the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, has produced an estimate of the number of plants known to science. By searching through existing databases, the researchers have estimated that there are now 390,900 known plant species, of which around 369,400 are flowering plants. But this figure is…
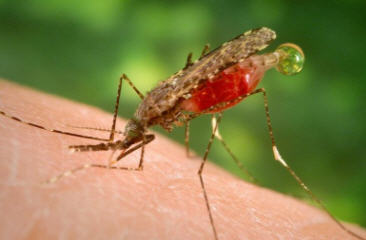
Malaria incidence and invasive plants – is there a link?
3.2 billion people are still at risk of getting malaria. Although progress has been made, if we are to achieve a 90% reduction in global malaria incidence and mortality by 2030 we must do more. Controlling invasive species may be part of the solution. The path will not be easy. Mosquitoes are becoming increasingly resistant…
New in January and February 2016 from the ISC
In January and February 2016 the following datasheets were published on CABI’s Invasive Species Compendium (ISC). You can explore the open-access ISC here: www.cabi.org/isc. Agropyron cristatum (crested wheatgrass) A. cristatum is a resilient and long-lived perennial grass with stems that are 20-70 cm long and with finely-branched deep roots that extend to a depth of 1 m. It…
New in November and December 2015 from the ISC
In November and December 2015 the following datasheets were published on CABI’s Invasive Species Compendium (ISC). You can explore the open-access ISC here: www.cabi.org/isc. Cotoneaster horizontalis (wall-spray) C. horizontalis is a woody, perennial, deciduous or semi-evergreen shrub with horizontally spreading branches, native to parts of China. It is an attractive garden plant with bright red berries…
New in October 2015 from the ISC
In October 2015 the following datasheets were published on CABI’s Invasive Species Compendium (ISC). You can explore the open-access ISC here: www.cabi.org/isc Rubus niveus (Mysore raspberry) Rubus niveus is an invasive blackberry which is threatening the endemic wildlife of the Galapagos Islands. More specifically, it is a threat to the unusual daisy tree forests (of…
New in September 2015 from the ISC
In September 2015 the following datasheets were published on CABI’s Invasive Species Compendium (ISC). You can explore the open-access ISC here: www.cabi.org/isc Verbascum thapsus (common mullein) A biennial herb which has naturalized in most temperate regions of the world. It grows vigorously, threatening native plants in meadows and forest gaps. Eradication is extremely difficult since…