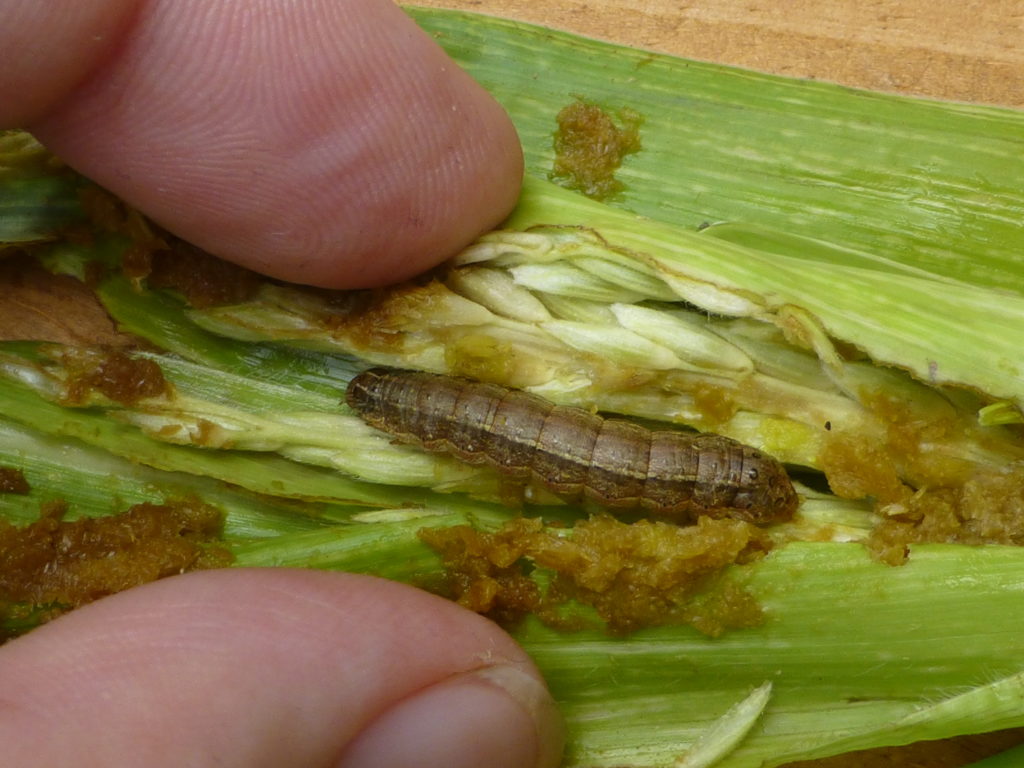
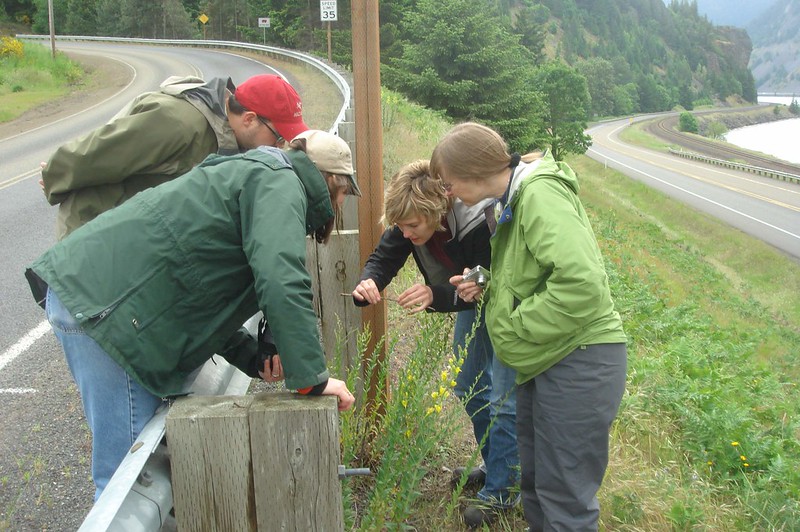
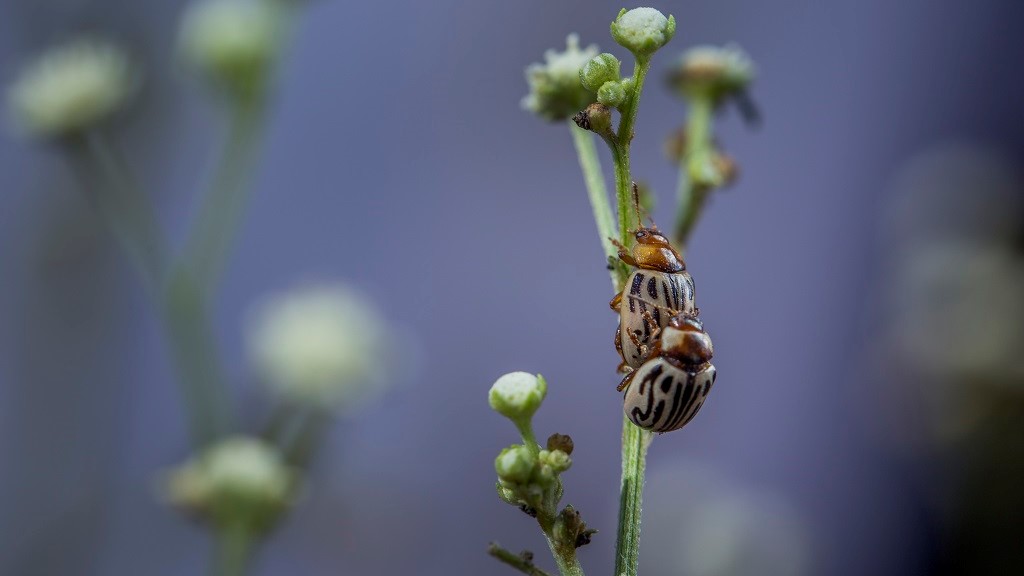
Busy in biocontrol: spotlight on weed researcher Jennifer Andreas
Meet Jennifer Andreas, who has collaborated with CABI on a number of biological control projects since 2000, in this profile originally published by the North American Invasive Species Management Association (NAISMA).
CABI supports first Dutch field trials with exotic insect to combat Japanese knotweed
For the first time in the Netherlands, an exotic insect species is released into the wild to combat a harmful plant species. The Japanese knotweed psyllid should offer relief against the rampant Asian knotweed. Suzanne Lommen of the Institute of Biology Leiden is coordinating the field trials as part of a consortium which includes CABI,…
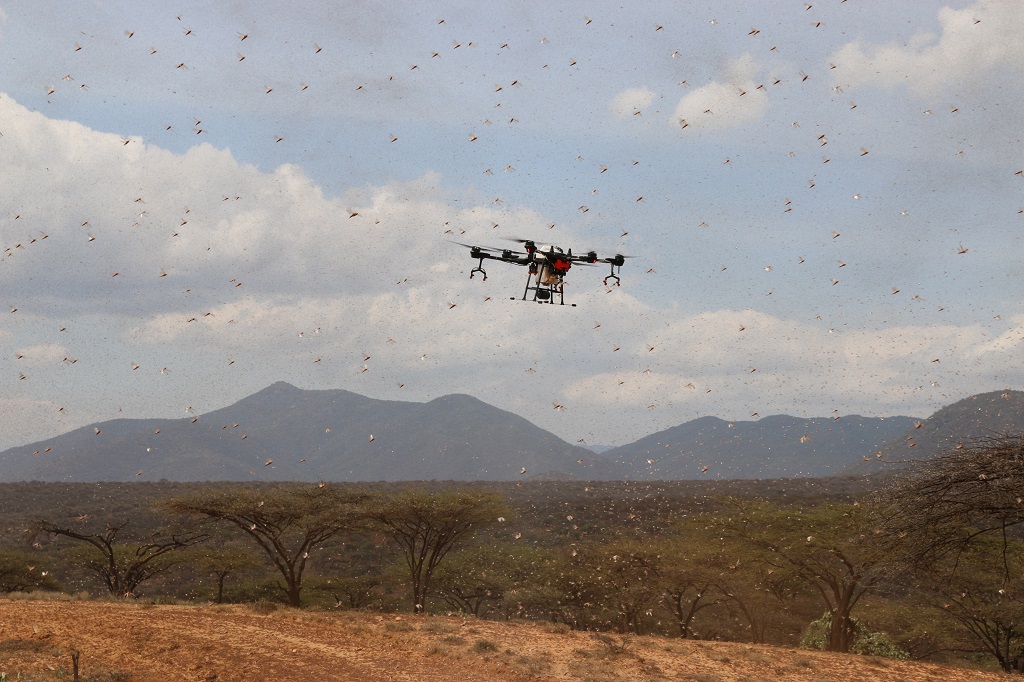
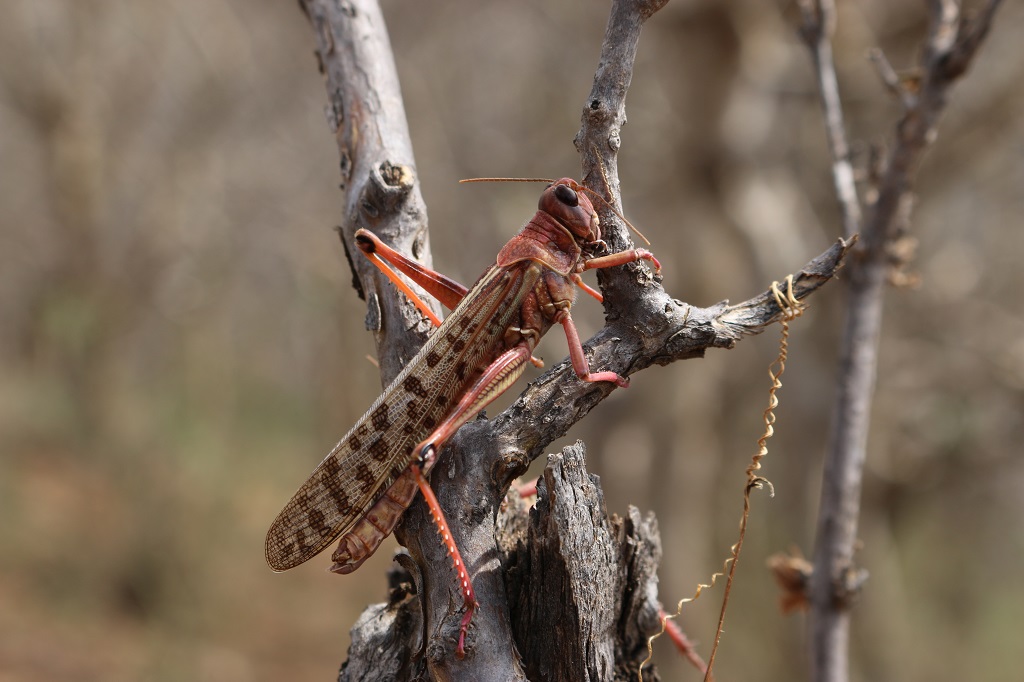
A plague during a pandemic: how to increase resilience against the desert locust outbreak
On 12 October, as part of a virtual side event for the World Food Prize’s annual Borlaug Dialogue, CABI hosted a panel session on A plague during a pandemic: how to increase resilience against the desert locust outbreak. The webinar aimed to communicate the urgent need for a comprehensive and coordinated response to this year’s…
Coronavirus and invasive species
This article was originally published on the CHAP blog. Dr Richard Shaw is Country Director and Regional Coordinator Invasives at CABI UK. Using his invasive species expertise, he examines the global spread of coronavirus
Do invasive species impact men and women differently?
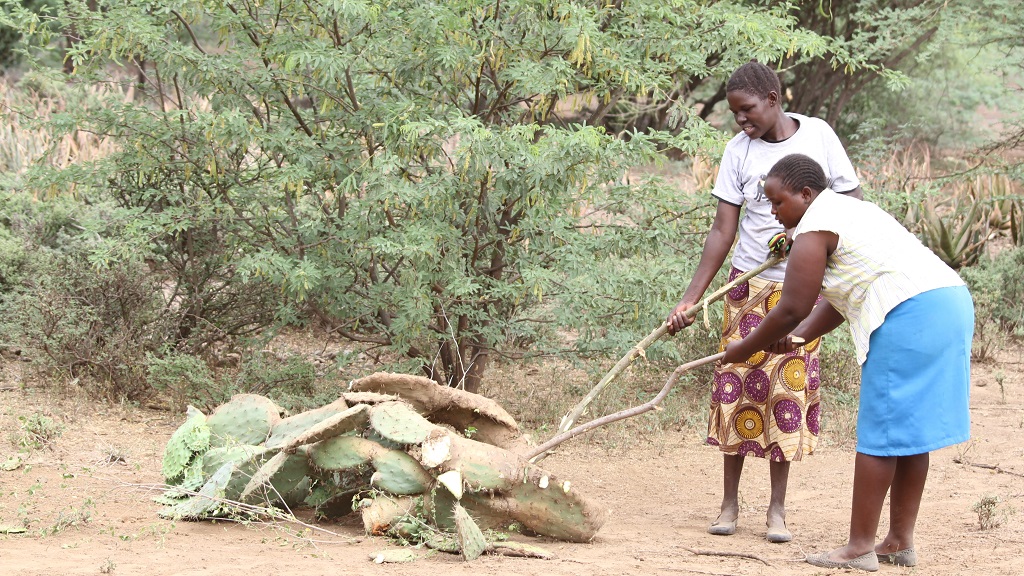
We know that invasive species – whose introduction and spread threaten biodiversity – disproportionately affect communities in poor rural areas who depend on agriculture and natural resources for their livelihood. But do gender roles and relationships in agriculture influence the way men and women experience the impact of invasive species?